Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that relocates hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to regions of hair loss.
While it can be an effective and permanent solution for baldness or thinning, the process is not without potential complications.
This article will explore two common issues – bumps and shedding – that may occur after a hair transplant, as well as when to seek medical attention and answers to frequently asked questions.
Click to find out how hair transplant works!
🌱 Hair Transplant Bumps: Causes and Treatments
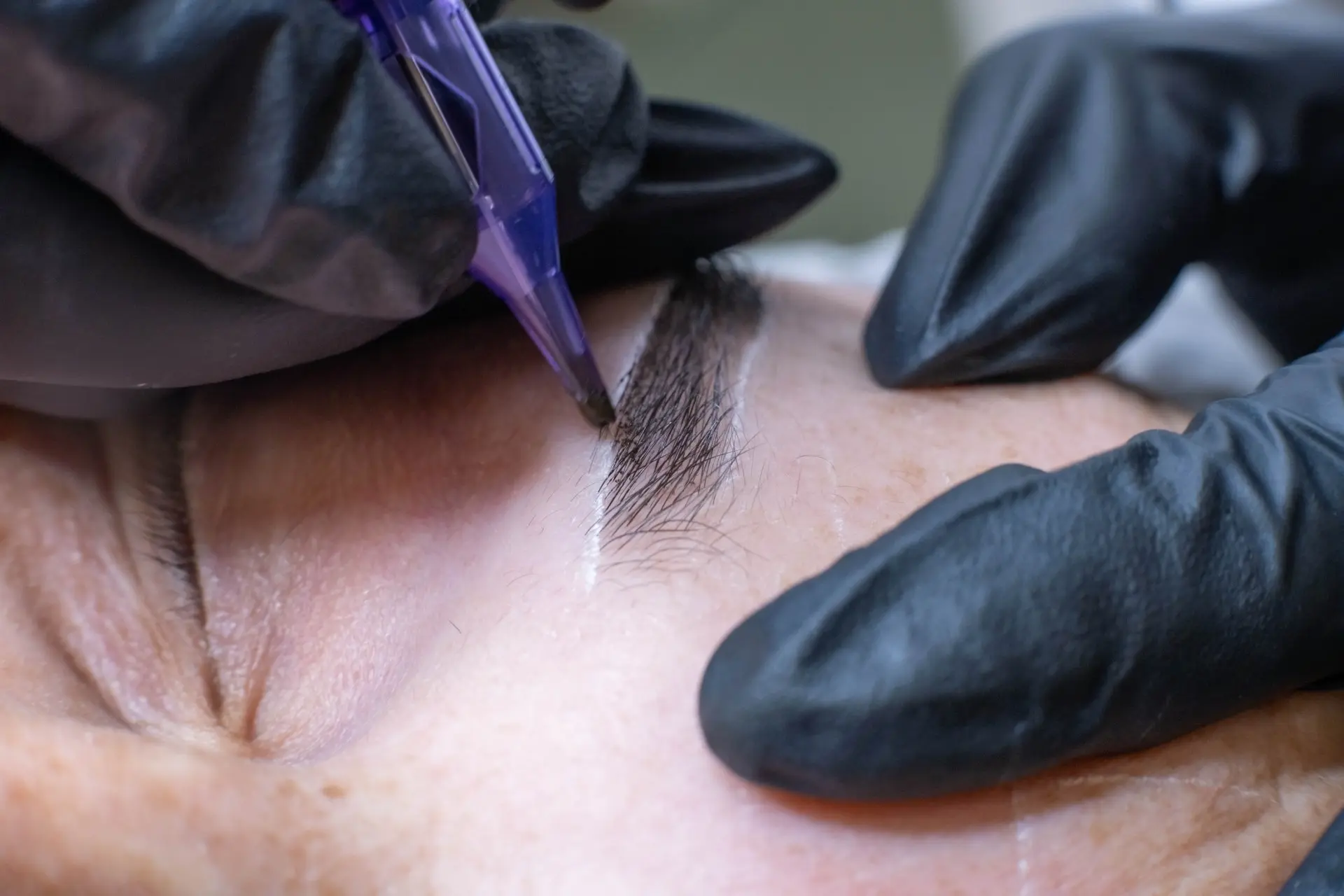
The appearance of small bumps or pimples in the recipient area is a potential complication following hair transplant surgery. These bumps, which may resemble folliculitis, are often the result of inflammation or ingrown hairs as the transplanted follicles begin to grow in their new location.
In the majority of cases, these bumps will resolve on their own within several weeks to a few months as the inflammation subsides and the hair shafts exit the skin.
❗ Gentle care of the area, including daily cleansing with mild soap and water, and avoidance of picking or scratching the bumps, can aid in the healing process.
However, if the bumps persist beyond a few months, and are also:
- Painful or tender,
- Or show signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or purulent discharge,
It is important to promptly seek evaluation by a qualified medical professional.
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include topical or oral antibiotics, steroid creams to reduce inflammation, or in some cases, surgical removal of the affected follicles.
Following post-operative care instructions closely and attending all scheduled follow-up appointments can help prevent and promptly identify any complications.
😱 Hair Fall After Hair Transplant→ The Normal Shedding Process
Another common occurrence that can be alarming for patients is shedding of the transplanted hairs within the first few months after surgery.
Known as “shock loss”, this temporary shedding typically begins around 2-8 weeks post-procedure and can affect both the transplanted and some of the native hairs in the recipient area.
Shock loss occurs because the transplanted follicles, which are traumatized during the surgical process, enter into a resting phase called telogen. This is a normal part of the hair growth cycle and does not indicate a failure of the transplant.
In fact, even with the shedding, the follicles remain viable and will begin to produce new hairs as they reenter the anagen, or growth phase.
Most patients will start to see new hairs growing from the transplanted follicles within 3-4 months after surgery.
By the 6-9 month mark, a significant improvement in hair density is usually evident, with about 60% of new hair growth.
Yet still, it can take 12-18 months to see the full, final results of the transplant. Therefore, patience is key, and shedding should not be a cause for panic in the early months after the procedure.
🩺 When to Seek Medical Help
While some degree of bumps and shedding are a normal and expected part of the hair transplant process, there are certain signs and symptoms that warrant prompt medical evaluation. These include:
- Excessive bleeding or foul-smelling discharge from the transplant sites
- Fever, chills, or other signs of systemic infection
- Severe or worsening pain, redness, or swelling at the surgical sites
- Rapid or progressive shedding that persists beyond 2 months post-procedure
- Poor or unsatisfactory hair growth in the transplanted areas 8-12 months after surgery
If any of these issues arise, it is important to contact a qualified medical professional promptly. They can evaluate the situation and recommend appropriate interventions, which may include antibiotics for infection, anti-inflammatory medications, surgical drainage or revision, or guidance on the expected timeline for results based on individual factors.
Get free medical consultation from Dr. Cengizhan right now!
❓ FAQ
- When is a hair transplant not possible?
A hair transplant may not be possible if there is:
- Insufficient donor hair
- Extensive scalp scarring
- Certain scalp skin conditions
- Underlying medical issues that impair healing.
A qualified surgeon like Dr. Cengizhan can determine candidacy during a consultation session.
- How can a beard transplant fail?
A beard transplant can fail due to:
- Poor surgical technique damaging follicles
- Inadequate blood supply to the transplanted area
- Infection causing graft loss or scarring
- Improper graft placement leading to unnatural results
- Patient non-compliance with post-op care
- Unrealistic expectations or insufficient donor hair
Choosing an experienced surgeon, following aftercare instructions, and having realistic expectations can help minimize the risk of failure.
Find out more about beard transplant success rate!
- Is FUE a scarless hair transplant surgery?
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) is not entirely scarless, but it leaves small, dot-like scars that are less noticeable than the linear scar from FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation), which is believed to be an outdated treatment nowadays. Proper technique and aftercare can minimize scarring to none.
- What is the difference between a hair transplant and FUE?
FUE is a type of hair transplant technique that involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area and transplanting them to the recipient site. Other techniques, like FUT, remove a strip of skin containing hair follicles for transplantation.
- What is the life of FUE hair transplant results?
FUE hair transplant results are considered permanent, as the transplanted hair follicles are genetically resistant to balding.
- What is the most advanced hair transplant?
Currently, FUE is considered one of the most advanced hair transplant techniques due to its minimally invasive nature, natural-looking results, and shorter recovery time compared to other methods like FUT.
- What is the process of FUE and FUT hair transplant?
In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area using a specialized punch tool and transplanted to the recipient site. FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and transplanting them to the recipient site.
- Where is the best place to get a hair transplant?
The best place to get a hair transplant is a reputable clinic with experienced, certified surgeons specializing in hair restoration. Look for clinics with a proven track record, positive patient reviews, and a willingness to show before-and-after photos!
- How to reduce skin redness after a hair transplant?
To reduce redness and promote healing, follow post-operative care instructions, apply cold compresses, sleep with your head elevated, and avoid direct sun exposure. Redness typically resolves within 1-2 weeks, but persistent or severe redness may require medical attention.
- Can you change your hair texture with a hair transplant?
A hair transplant cannot change your hair texture, as the transplanted follicles maintain the same characteristics as the donor area. However, in some cases, transplanting finer hairs from the back or sides of the scalp can create a more natural-looking hairline or crown.
Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547754/